Page 94 - Libro Memoria Cien Inglés
P. 94
as well as to define endophenotypes reveal a difference of 4 to 5.5 years in
based on genetic variations and spe- the median age of onset of patients
cific and measurable characteristics of with Alzheimer's disease in subjects
patients and controls based on clinical with APOE ɛ4. This study allows us to
neuroimaging, biochemical or patholo- refine the study of the molecular me-
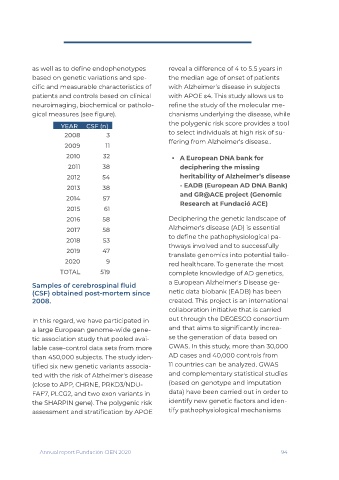
gical measures (see figure). chanisms underlying the disease, while
YEAR CSF (n) the polygenic risk score provides a tool
2008 3 to select individuals at high risk of su-
ffering from Alzheimer's disease..
2009 11
2010 32 • A European DNA bank for
2011 38 deciphering the missing
2012 54 heritability of Alzheimer’s disease
2013 38 - EADB (European AD DNA Bank)
2014 57 and GR@ACE project (Genomic
Research at Fundació ACE)
2015 61
2016 58 Deciphering the genetic landscape of
2017 58 Alzheimer's disease (AD) is essential
2018 53 to define the pathophysiological pa-
thways involved and to successfully
2019 47 translate genomics into potential tailo-
2020 9 red healthcare. To generate the most
TOTAL 519 complete knowledge of AD genetics,
Samples of cerebrospinal fluid a European Alzheimer's Disease ge-
(CSF) obtained post-mortem since netic data biobank (EADB) has been
2008. created. This project is an international
collaboration initiative that is carried
In this regard, we have participated in out through the DEGESCO consortium
a large European genome-wide gene- and that aims to significantly increa-
tic association study that pooled avai- se the generation of data based on
lable case-control data sets from more GWAS. In this study, more than 30,000
than 450,000 subjects. The study iden- AD cases and 40,000 controls from
tified six new genetic variants associa- 11 countries can be analyzed. GWAS
ted with the risk of Alzheimer's disease and complementary statistical studies
(close to APP, CHRNE, PRKD3/NDU- (based on genotype and imputation
FAF7, PLCG2, and two exon variants in data) have been carried out in order to
the SHARPIN gene). The polygenic risk identify new genetic factors and iden-
assessment and stratification by APOE tify pathophysiological mechanisms
Annual report Fundación CIEN 2020 94